What is the Best Pre-Workout Powder?
What is the Best Pre Workout Powder? Introducing Time 4 Pre Workout Professional
What is the Best Pre Workout?
(Click On The Reference Numbers In Blue For More Info)
Here at Time 4 Nutrition, we take an evidence-based approach to the development of all our products. We make no outlandish claims but just state the findings of published studies which have investigated the efficacy of the ingredients we use. Therefore, you can be secure in the knowledge that everything we recommend is supported by evidence. We also understand that science changes. Consequently, we change our formulations and develop new products in accordance with advances in understanding to keep you at the cutting edge. So, we are proud to announce the launch of Time 4 Pre Workout Professional, one in a new generation of Time 4 Nutrition products.
In order for us to maximise the benefits from our training, we need to be fully prepared both physically and mentally to meet the demands and challenges of each workout. This means having sufficient levels of energy and being highly focused. However, no matter how motivated we are, at times this can be difficult, particularly when trying to balance the demands of life, work, and training.
This is where Time 4 Pre Workout Professional can be a valuable addition to your nutrition strategy. This specially selected combination of substances has been formulated for use before intense workouts. Its key ingredients have been shown scientifically to provide a number of potential benefits for performance.
These include, but are not limited to:
• Increasing muscular strength (1, 2, 5, 6, 45, 48,49,51,64)
• Increasing training volume (16, 25,26)
• Increasing muscle mass (17,31)
• Increasing Anaerobic Power (1,45, 49, 64)
• Increasing muscular endurance (6, 12, 18, 19, 25,26, 45)
• Increasing Fat Metabolism during exercise (3, 14,61)
• Increasing growth hormone levels (51, 52)
• Increasing testosterone levels (55)
• Sparing Glycogen during exercise (3)
• Increasing aerobic endurance performance (3, 8, 10, 11, 15, 29, 45)
• Increasing running performance (4,15)
• Improved cognitive performance (7,18, 35,36,37, 38,39,40,41,42, 53,56,57,59)
• Improved neuromuscular co-ordination (54,56)
• Increasing vigilance (4)
• Improving Reaction Time (7,42, 53,60)
• Increasing Energetic Arousal (7, 20, 21, 53)
• Increasing motivation to train (50, 53,58)
• Reducing feelings of fatigue (16, 28, 30, 56,58,62)
• Delaying fatigue during exercise (8, 9, 11, 12, 18, 19, 53,57)
• Reducing the build up of Blood Lactate (9, 11 15, 22, 33)
• Decreasing post-exercise muscle soreness (30)
• Enhancing Vasodilation to increase blood flow to the muscles (34)
What’s in Time 4 Pre-workout Professional?
Time 4 Pre-Workout Professional is a specially formulated blend of Citrulline Malate, Beta Alanine, L-Tyrosine, Alpha GPC, Caffeine Anhydrous, Kigelia Africana, Theacrine, Hordenine, AstraGin®, and Huperzine A.
As we look at each of these pre workout ingredients in-depth, and a selection of the research that supports their use, you’ll begin to see why Time 4 Pre-Workout Professional is such a great product and how it may benefit you.

What is Beta-Alanine?
Beta-alanine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that the body is able to produce it, and it occurs naturally in some food, with meat, poultry and fish being the best sources. However, it is is often taken in supplement form, as its increased intake is associated with a number of benefits for health and performance. These include increasing muscle mass, muscular endurance, VO2max,, and time to exhaustion during prolonged high intensity exercise, and reducing fatigue and blood lactate levels during exercise. It also plays a role in immunity and attenuating oxidative stress, and benefits muscle function in older adults.
What does the science say about Beta-Alanine and exercise?
Beta-alanine is rapidly developing as a popular ergogenic pre workout supplement for athletes worldwide, and the current scientific literature suggests that its use is based on sound evidence.
For example, a study by Hill et al., (13) on competitive cyclists found that just four weeks of supplementation with beta-alanine increased total work completed by 13%, with a further 3.2% increase after 10 weeks.
Baguet and colleagues (14) investigated the effects of beta-alanine supplementation on rowing performance. 18 rowers who supplemented with beta-alanine for seven weeks were 4.3 seconds faster than the placebo group in a 2,000-meter race lasting over 6 minutes, whereas prior to supplementation they were 0.3 seconds slower. While the results of a study by Santana (15) showed that beta-alanine supplementation improved 10km running time and reduced lactate levels.
Beta-alanine supplementation has also been shown to enhance resistance exercise performance. For example, a study by Hoffman and colleagues (16) examined the effects of 30 days of beta-alanine supplementation in college football players. The results showed that those subjects supplementing with beta-alanine achieved a significantly higher training volume for all resistance exercise sessions compared to a placebo. In addition, subjective feelings of fatigue were significantly lower for the beta-alanine group than the placebo.
Not only has beta-alanine supplementation been shown to improve exercise performance, but there is also evidence to suggest that it can increase muscle mass in response to training. Kern and Robinson (17) investigated the effectiveness of beta-alanine as an ergogenic aid in previously trained college wrestlers and football players. In the wrestlers’ group both those participants taking the placebo and supplement lost weight, which was the goal; however, those supplementing with beta-alanine increased lean mass by 1.1lb (0.5kg), whereas the placebo group lost lean mass (0.4kg). In the football group both those taking the supplement and the placebo gained weight; however, the supplement group gained an average of 1kg lean mass compared to 0.5kg for the placebo group.
Optimal performance often involves non-physical aspects, such as focus. Studies conducted on tactical athletes and military personnel during high-intensity conditions, have shown beta-alanine supplementation to improve focus, alertness, and cognitive functioning. For example, Hoffman and colleagues (18) found that beta-alanine supplementation not only improved the 50 metre casualty carry assessment times of military personnel, but also their cognitive performance during a 2 minute serial subtraction test at a shooting range under continuous fire.
How does Beta-Alanine enhance performance pre workout?
Unlike most amino acids, beta-alanine is not used by the body to synthesise proteins but instead works together with the amino acid histidine to produce a substance known as carnosine, which is stored in skeletal muscles.
Although the mechanism by which chronic beta-alanine supplementation has an ergogenic effect is widely debated, Bellinger (22) suggests the popular view is that it augments intramuscular carnosine content, leading to an increase in muscle buffer capacity, a delay in the onset of muscular fatigue, and enhanced recovery during repeated bouts of high-intensity exercise. Hence beta-alanine supplementation appears to be most effective for exercise that relies heavily on energy production from anaerobic glycolysis.
In other words, the breakdown of glucose to fuel high intensity exercise results in an increase in a substance known as lactate within the muscles. This leads to an increase in acidity, which blocks further glucose breakdown and reduces muscles’ ability to contract, causing fatigue. Carnosine acts as a buffer to reduce the acidity in muscles and so delay fatigue thereby improving athletic performance.
Histidine levels are normally high within the muscles while beta-alanine levels are low, which limits the production of carnosine. However, supplementing with beta-alanine has been shown to elevate carnosine levels in muscles by 80% (23).
Beta-alanine has also been shown to enhance endurance performance by increasing VO2max, the body’s maximum rate of oxygen consumption. Ghiasvand and colleagues (24) investigated the effects of beta-alanine supplementation on VO2max, time to exhaustion and lactate concentrations in male physical education students during a continuous graded exercise test. Participants supplemented with either beta-alanine or placebo for 6 weeks prior to the test. The results showed that supplementation with beta-alanine produced a significant increase in VO2 max and a significant decrease in lactate concentrations, both of which enhance endurance performance.

What is Citrulline Malate?
Like beta-alanine, citrulline is also a non-essential amino acid, which occurs in a limited number of foods, primarily watermelon. It is often consumed in supplement form, as higher levels have been shown to have beneficial effects on health and exercise performance. These include increasing dilation of the blood vessels to enhance blood flow and reduce blood pressure, enhancing muscle endurance, reducing fatigue and post exercise muscle soreness, and increasing strength and muscle growth, improving aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance.
There are two major forms of citrulline used in dietary supplements. These are L-citrulline, which is citrulline by itself, and citrulline malate. This is a combination of citrulline and another compound called malate, or malic acid, which is found in fruits such as apples and helps to enhance the effects of citrulline. It also plays an important role in aerobic energy production where oxygen and a carbon compound (acetyl Co-A) are used to produce to energy. Citrulline malate is more commonly used in sports supplements and is the form contained in Time 4 Pre-Workout Professional.
What does the science say about Citrulline and exercise?
Citrulline’s potential performance enhancing properties were largely ignored until the last decade when it began to emerge as a highly promising supplement as its role in aerobic and anaerobic performance, blood pressure, strength, power, and endurance were investigated. There are now many studies demonstrating its performance benefits.
For example, Wax et al., (25) investigated the efficacy of citrulline malate supplementation on the exercise performance of advanced male weightlifters. Subjects performed 5 sequential sets (60% 1 repetition maximum) to failure on the leg press, hack squat, and leg extension machines. The results showed that those participants supplementing with citrulline malate were able to perform a significantly higher number of repetitions during all 3 exercises compared with the placebo group.
Similar results were obtained by Perez-Guisado and Jakeman (26) who found that citrulline malate enhances anaerobic exercise performance, in the form of the number of repetitions of bench press to failure, with those subjects supplementing with citrulline malate being able to perform 52% more repetitions in their last set compared to a placebo.
The benefits of citrulline malate supplementation are not just not limited to men, as Glen and colleagues (27) showed that acute citrulline malate supplementation in resistance trained females enhanced performance as indicated by an increase in total repetitions performed and decreased levels of perceived exertion.
Aerobic exercise performance has also been shown to benefit from citrulline malate supplementation. For example, Bendahan and colleagues (28) investigated the effects of citrulline malate supplementation on muscle energetics and found that it resulted in a 34% increase in the rate of oxidative ATP production during exercise, and a 20% increase in the rate of phosphocreatine recovery after exercise, indicating a larger contribution of oxidative ATP synthesis to energy production. A significant reduction in the sensation of fatigue was also observed.
The enhanced energy production capacity provided by citrulline supplementation has been shown to translate directly into improved aerobic exercise performance. Suzuki and colleagues (29) found that participants supplementing with citrulline reduced the time taken to complete a cycling ergometer time trial. Participants also reported improved subjective feelings of muscle fatigue and concentration immediately after the exercise.
Muscle soreness can not only be a pain literally, but can also hinder our ability to train, necessitating longer recovery periods between workouts. However, research shows that citrulline malate supplementation can contribute to a significant reduction in muscle soreness.
A systematic review and meta-analysis by Rhim et al., (30) which included 13 eligible articles involving a total of 206 participants, showed that citrulline supplementation significantly reduced feelings of exertion and muscle soreness 24 and 48 hours post-exercise. Other studies have shown this reduction in muscle soreness to be as great as 40% at 24 hours and 48 hours after a training session (26).
How does Citrulline Malate enhance performance?
Citrulline malate appears to enhance performance in a number of ways:
Firstly, it increases vasodilation, i.e., widening of arteries and veins, which helps to lower blood pressure, but also increases blood flow to the working muscles.
It does this by working with another amino acid, arginine, to form a molecule called nitric oxide (NO), which causes vasodilation of blood vessels by relaxing the smooth muscle cells in the walls of the blood vessels. This increase in blood in the muscle when exercising is referred to as the ‘pump.’ Interestingly, consuming citrulline increases arginine in the body more than consuming arginine itself (34).
Citrulline may also contribute to muscle growth. Although citrulline is not an amino acid used directly to build proteins, it has been shown to increase protein synthesis by stimulating an important signalling pathway involved in muscle building. It may also reduce the liver’s uptake of certain amino acids and prevent their breakdown (31). This is because citrulline is not taken up by the liver, its synthesis from arginine, glutamine, ornithine and proline in the intestine prevents the liver’s uptake of the two first amino acids which prevents amino acid catabolism. This sparing effect may contribute to increased muscle protein synthesis, muscle protein content and performance (31).
Citrulline-malate supplementation can also increase the use of amino acids, especially the branched chain amino acids during exercise and enhance the production of arginine-derived metabolites such as creatinine, which plays an important role in exercise. It has also been associated with increased post-exercise growth hormone levels (32).
Sufficient energy stores are essential for optimal exercise performance. Supplementation with citrulline malate has been shown to increase in the rate of oxidative ATP production during exercise (28).
It has also been shown to contribute to exercise performance by reducing lactate levels which helps to postpone fatigue during high intensity or prolonged activity (33).
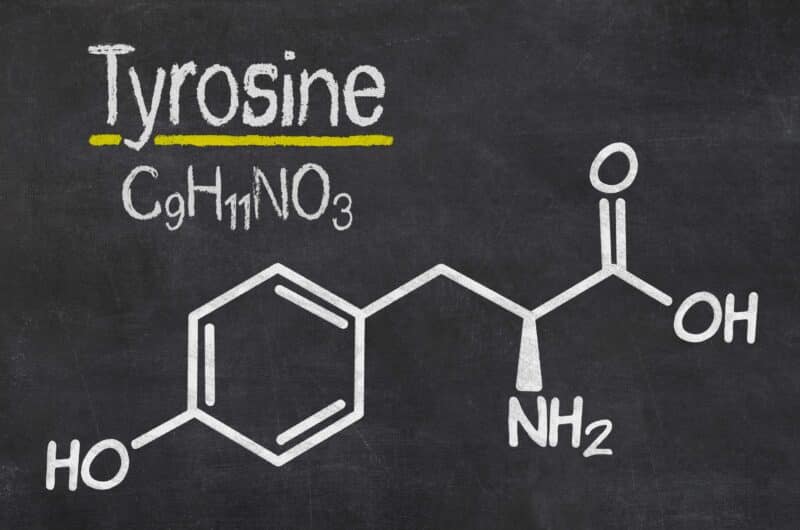
What is L-Tyrosine?
L-tyrosine is a non-essential amino acid synthesized in the body from the amino acid L-phenylalanine. It is also found in chicken, turkey, fish, dairy products and most other high-protein foods. It is involved in the structure of almost every protein in the body, and is an essential component for the production of several important brain chemicals known as neurotransmitters, which help nerve cells to communicate. These include epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine. Dopamine regulates the reward and pleasure centres in the brain, and plays an important role in memory and motor skills. While epinephrine and norepinephrine are the hormones responsible for the fight-or-flight response to stressful situations. They are released during exercise and increase in line the with intensity and duration of exercise. Tyrosine also plays a role in the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for hair and skin colour, and aids the function of organs responsible for making and regulating hormones, including the adrenal, thyroid, and pituitary glands.
What does the science say about L-Tyrosine and exercise?
There is something of a tendency to focus on the physical aspects of performance, such as strength, power, and endurance, but the optimal performance of many activities requires increased levels of cognitive function. Supplementation with tyrosine has been shown to improve various aspects of this, such as alertness, attention, and focus, amongst other exercise related benefits, under various conditions.
For example, the results of a review by Jongkees et al., (35) showed that tyrosine supplementation is an effective method for enhancing cognitive performance, particularly in short-term stressful and/or cognitively demanding situations.
Hase and colleagues (36) conducted a systematic review to examine the effects of tyrosine on behaviour and cognition. The results showed that tyrosine supplementation counteracts reductions in working memory, which plays an important role in concentration and the ability to follow instructions, and information processing that are induced by demanding conditions such as extreme weather or cognitive load.
Tyrosine supplementation has also been shown to enhance cognitive flexibility. This is the ability to switch between tasks or thoughts. The quicker a person can switch tasks, the greater their cognitive flexibility (37).
The negative effects of sleep deprivation on various aspects of physical and mental performance are well documented. Neri et al., (38) examined the behavioural effects of tyrosine during an episode of continuous nighttime work involving one night’s sleep loss. Subjects performed a battery of performance tasks and mood scales for approximately 13 hours. They remained awake throughout the day on which the experiment began and were awake for more than 24 hours by the end of testing. Six hours after the experiment began, one-half of the subjects received a tyrosine supplement while the other half received a placebo. Tyrosine was associated with a significant improvement in the usual performance decline on a psychomotor task and vigilance task.
Various studies (39, 40, 41) have shown tyrosine supplementation to be particularly effective at enhancing cognitive performance in challenging environments such as extremes of temperature, both hot and cold. For example, Banderet and Lieberman (41) found that tyrosine supplementation significantly decreased symptoms, adverse moods, and performance impairments in participants who were subjected to 4.5 hours of exposure to cold and hypoxia (inadequate oxygen levels).
O’Brien and colleagues (39) found dietary tyrosine supplementation is effective for mitigating cold-induced cognitive performance such as working memory, even with reduced core temperature.
At the other extreme of temperature, Coull et al., (42) investigated the effects of tyrosine ingestion on cognitive and physical performance during soccer-specific exercise in a warm environment. The results showed that tyrosine supplementation was associated with improved vigilance and reaction time in comparison to a placebo.
Tyrosine supplementation has been shown to not only enhance cognitive function in the heat, but also physical performance. The results of a study by Tumility et al., (20), which involved participants cycling to exhaustion in a temperature of 30°C and 60% relative humidity, showed that tyrosine supplementation allowed participants to cycle for significantly longer (80 minutes vs. 69.2 minutes) compared to a placebo.
How does Tyrosine improve performance pre workout?
Although still not fully understood, a number of mechanisms have been proposed to explain tyrosine’s positive effects on performance.
Acutely stressful situations can disrupt performance and deplete levels of the neurotransmitters, norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain (41). As tyrosine is the precursor to dopamine and norepinephrine, it is suggested that increasing tyrosine uptake may improve cognitive performance by counteracting depleted levels of these neurotransmitters (36).
With regard to tyrosine’s role in enhancing exercise endurance in the heat, recent findings suggest that dopamine and epinephrine influence the function of hypothalamus, the thermoregulatory centre in the brain, which contributes to the control of body temperature whilst at rest and during exercise (43).
Additionally, low dopamine levels are associated with fatigue, which leads to a reduction in exercise intensity or cessation of exercise, thereby limiting performance (44). Consequently, ensuring adequate dopamine levels are likely to contribute to a reduction in fatigue.

What is Caffeine Anhydrous?
Caffeine is an organic compound which occurs naturally in various plants, such as tea, coffee, and cocoa, and acts as a central nervous system stimulant.
It is the world’s most widely consumed psychoactive substance, with approximately 90% of adults In Western countries consuming caffeine on a regular basis.
It is most frequently consumed in the form of beverages such as coffee, soft drinks and tea, and increasingly in functional beverages, such as energy drinks, and other caffeine-containing products, including ‘pre-workout supplements’, energy gels, etc.
Caffeine anhydrous is made from the seeds and leaves of coffee plants. The term ‘anhydrous’ simply means without water. Caffeine is extracted from the plant material and then dehydrated, which produces a more potent and highly concentrated form of caffeine powder.
Caffeine consumption is associated with increases in muscular strength and endurance, anaerobic power, aerobic performance, fat oxidation, vigilance, and arousal. It is also associated with reductions in fatigue and reaction time.
What does the science say about Caffeine and exercise?
The difficulty in citing specific studies to support the use of caffeine as an ergogenic aid is not that there is a lack of information regarding its efficacy; rather, there is an overabundance. Just a quick Google search using the terms “caffeine,” “exercise,” “research” produces approximately 17,100,000 results.
Fortunately, the International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) (45) has critically evaluated the available literature to date and produced a position stand on the use of caffeine. This states that supplementation with caffeine has been shown to enhance various aspects of exercise performance. These include, but are not limited to muscular endurance, movement velocity and muscular strength, sprinting, jumping, and throwing performance, as well as a wide range of aerobic and anaerobic sport-specific activities. The use of caffeine in conjunction with endurance exercise in the heat and at altitude is also well supported.
Caffeine’s ergogenic effect is not confined to the physical aspects of performance, as it has shown to have a positive effect on cognitive function, including attention and vigilance, and may improve cognitive and physical performance in individuals under conditions of sleep deprivation. Interestingly, it appears to improve physical performance in both trained and untrained individuals.
Here are just a few brief examples of the many studies supporting the use of caffeine.
A review and meta-analysis by Grgic and colleagues (46), which involved 20 studies, found that caffeine ingestion improved both muscular strength and power.
Spriet et al., (3) investigated the effects of caffeine on aerobic endurance performance and muscle metabolism during prolonged exercise. Eight subjects cycled to exhaustion at approximately 80% maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) 1 hour after ingestion of a placebo or caffeine. The subjects in the caffeine trial cycled significantly longer (96 minutes) in comparison to the placebo trial (76 minutes). The results indicate that caffeine supplementation before exercise decreased the breakdown of muscle glycogen by approximately 55% over the first 15 minutes of exercise. This ‘spared glycogen’ was then available later in the exercise and was associated with a prolonged time to exhaustion. In short, caffeine helped the body to use fat as energy source and so spare the muscles’ stores of glucose, allowing them to be used later to extend the exercise time.
Wolf and colleagues (1) compared the effects of caffeine and placebo on anaerobic exercise performance. Participants using caffeine were able to lift more total weight for the chest press exercise and attain greater peak power during the Wingate test. This is an exercise test that measures peak anaerobic power and anaerobic capacity.
The results of a study by Doyle and colleagues (7) showed that caffeine had a positive effect on arousal, response time, accuracy, and performance in fencers.
How does Caffeine enhance performance pre workout?
Unlike most other substances, caffeine enhances performance by exerting an influence on a variety of cells in the body via a range of mechanisms.
For example, caffeine provides its stimulant effect by mimicking a substance known as adenosine, which is structurally similar. In the brain adenosine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. This means, it can act as a central nervous system depressant. In normal conditions, it promotes sleep and suppresses arousal (8).
Caffeine is able to mimic adenosine so effectively that it can attach to adenosine receptors in the brain and block its uptake. Instead of slowing down because of the adenosine’s effect, the nerve cells are stimulated, which improves focus and energy while reducing tiredness. This effect is further increased by enhancing the release of other naturally occurring stimulants, including dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine.
Caffeine helps to enhance endurance performance by promoting the increased utilisation of fat as an energy source while inhibiting carbohydrate breakdown, allowing it to be used for energy later, thereby improving endurance (3).
It appears to improve muscular performance through activation of both the central (47) and peripheral nervous systems (2); however, the exact mechanisms responsible are still not fully understood.

What is Alpha-GPC?
L-alpha-glycerylphosphorylcholine (Alpha-GPC) is substance that occurs naturally in the body. It is a precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which helps nerve cells to communicate and so is essential in both brain and muscle tissue. Consequently, it plays an important role in many functions in the body including movement and elements of cognition, such as arousal, attention, motivation, and working memory.
As acetylcholine plays such an important role, but can’t be taken directly as a dietary supplement, methods of increasing acetylcholine levels have gained interest. One way is to consume foods that are high in choline, an essential nutrient that can be converted into acetylcholine. For example, these include beef liver, quinoa, kidney beans and shiitake mushrooms. A more convenient method is to consume a supplement. Alpha-GPC is one of the most popular due to its high choline content and easy absorption, with many studies to support its use. When taken supplementally, Alpha-GPC is converted to phosphorylcholine, which is the metabolically active form of choline.
What does the science say about Alpha-GPC and exercise?
Supplementation with Alpha-GPC has been shown to enhance both the physical and cognitive components of performance. For example, Bellar and colleagues (48) found that supplementation with Alpha-GPC produces a significant increase in isometric strength in comparison to a placebo. While Marcus et al., (49) noted Alpha-GPC’s ability to enhance maximum velocity and maximum mechanical power on the countermovement jump test, an assessment of lower body strength and power.
In addition to its role as a precursor of acetylcholine, Alpha-GPC has a role in dopamine and serotonin function. These neurotransmitters are related to feelings and emotions, including motivation, which is essential for optimising performance and maintaining long-term participation in exercise. Tamura and colleagues (50) investigated changes in the feelings of healthy volunteers before and after administering Alpha-GPC. The results showed that regular supplementation increased motivation significantly greater than a placebo.
Many of the positive adaptations to exercise, particularly resistance exercise training, i.e., increased muscle mass and strength and a reduction in fat mass, are due, in part, to exercise-induced increases in growth hormone.
Ziegenfuss and colleagues (51) investigated the effects of Alpha-GPC on serum growth hormone (GH) levels and exercise performance. Using a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover design, seven men with at least two years of resistance training experience ingested either Alpha-GPC or a placebo 90-minutes prior to training.
The results showed that compared to baseline (pre) values, peak growth hormone levels increased 44-fold with Alpha-GPC in comparison to just 2.6-fold with the placebo. Peak bench press force was 14% greater in Alpha-GPC in comparison to the placebo. Higher peak bench press power and increased post exercise fat metabolism were also noted in the Alpha-GPC group.
The results of a study Kawamura et al., (52) not only showed that supplementation with Alpha-GPC increased growth hormone levels significantly, whereas no significant change was observed with the placebo, there was a significant increase in choline levels and fat oxidation, while no such changes were observed with the placebo.
Alpha-GPC has also been shown to work well with other ingredients in Time 4 Pre-workout Professional. For example, Hoffman and colleagues (53) examined the effect of acute and prolonged (4-weeks) ingestion of a supplement comprising a L-tyrosine, anhydrous caffeine, and Alpha-GPC, amongst other ingredients, designed to improve reaction time and subjective measures of alertness, energy, fatigue, and focus in comparison to a placebo.
After consuming the supplement or a placebo, the subjects completed a questionnaire on subjective feelings of energy, fatigue, alertness and focus (PRE) then performed a 4-minute quickness and reaction test followed by a 10-min bout of exhaustive exercise. The results demonstrate that acute ingestion of the supplement, maintained reaction time, and feelings of focus and alertness to both visual and auditory stimuli following exhaustive exercise.
How does Alpha-GPC enhance performance pre workout?
Evidence suggests that alpha-GPC exerts its effects by increasing the synthesis and release of acetylcholine in the brain, where it is involved in memory, motivation, arousal, and attention (50)
With regards to physical performance, acetylcholine is also responsible for the nerve stimulation that causes muscles to contract. Therefore, it has been theorised that increased acetylcholine levels lead to a stronger signal for muscle contraction and, consequently, increased force production.

What is Kigelia Africana?
Kigelia africana is an African plant which is used widely in indigenous medicine to aid the healing of wounds and to treat a range of conditions, such as kidney and urinary complaints, rheumatism, psoriasis, and digestive ailments. It is also used as an aphrodisiac and for skin care, and has been shown to be possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and stimulatory properties.
What does the science say about Kigelia Africana and exercise?
Although not widely researched currently, Kigelia africana’s performance enhancing properties are beginning to gain greater recognition as it has become the subject of more rigorous scientific investigation. Consequently, it is being used increasingly in pre-workouts supplements due to proposed efficacy as central nervous system stimulant. For example, a study by Owolabi and colleagues (54) found that Kigelia Africana was a more effective stimulant than caffeine. The results of the study showed that it also enhanced muscle co-ordination, an important component of physical performance.
Another potentially performance enhancing effect of Kigelia Africana was highlighted in a study by Azu et al., (55), which showed that supplementation increased levels of the highly anabolic hormone, testosterone.
How does Kigelia Africana enhance performance pre workout?
The evidence suggests that Kigelia Africana possesses central nervous system stimulating properties which probably act by adhering to the adenosine receptors, like caffeine, leading to an increase in norepinephrine secretion and enhanced neural activity in numerous areas of the brain (54).
The precise mechanism behind Kigelia Africana’s ability to increase testosterone is not fully understood but is believed to be related to its antioxidant properties which may protect against testicular damage. It may also possess androgen-stimulating properties (55).

What is Threacrine?
Theacrine is a naturally occurring substance found in certain plants, with high levels present in the leaf of the wild tea plant species Camellia kucha Hung T. Chang. It can be considered to be a structurally modified version of caffeine, as it appears to be synthesized from caffeine in some plants and evidence suggests that it activates similar signalling pathways. It has been attracted considerable attention from the scientific community due to its diverse health benefits. These include antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, movement activation and fatigue reduction, enhanced cognitive performance, and improved lipid metabolism (56).
What does the science say about Theacrine and exercise?
A number of studies have demonstrated the potential positive effects of theacrine on exercise performance. Bello et al., (57) compared the effects of theacrine and caffeine on cognitive performance and time-to-exhaustion during a simulated soccer game in high-level male and female athletes. The results showed that supplementation with theacrine increased time to exhaustion by an average of 27% in comparison to a placebo while caffeine produced an average increase of 32%. The greatest improvement (38%) was achieved with a combination of theacrine and caffeine. This combination also provided greater improvements in cognitive function than either supplement independently.
We all probably experience times when we struggle to exercise due to a lack of focus, motivation, and energy. It is at these times that theacrine and can be particularly beneficial. For example, Ziegenfuss and colleagues (58) found that supplementation with theacrine increased energy, focus, concentration, willingness to exercise, and motivation to train from baseline values in comparison to a placebo.
Kuhman et al., (59) achieved similar results when they investigated the effects of a theacrine-containing dietary supplement with caffeine and placebo on energy, mood, and cognitive performance. The results showed that supplementation with theacrine increased alertness, focus, and energy in comparison placebo and to a greater degree than caffeine. It also reduced lethargy and grogginess in comparison to a placebo and caffeine.
How does Theacrine enhance performance pre workout?
Theacrine appears to exert its influence through several mechanisms; however, like caffeine, and Kigelia Africana, its most important effect is to counteract adenosine in the brain to produce a stimulatory effect. This is because the theacrine molecule is structurally similar to both caffeine and adenosine, therefore is able to bind to the adenosine receptors on the surface of cells to inhibit the action of adenosine.
In addition, theacrine is believed to affect a number of other neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, serotonin, and, norepinephrine, and help to restore levels of fatigue-related neurotransmitters in the brain, such as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HTP) and dopamine and their metabolites. It may also help to regulate brain glucose metabolism (56).

What is Hordenine?
Hordenine is a naturally occurring substance found in a variety of plants including barley (Hordeum vulgare) from where it takes its name, sprouted barley, and malt algae, cacti, some grass species and bitter orange. It has been shown to have an adrenergic effect. Adrenergic substances stimulate the sympathetic nervous system . This system helps regulate the body’s reaction to stress and exercise, as it contributes to an increase heart rate, sweating, and breathing rate while decreasing digestion. Hordenine is commonly used in many dietary supplements for its central nervous system stimulating properties both to promote athletic performance and aid fat loss by increasing metabolism.
What does the science say about Hordenine and exercise?
A number of studies have investigated the performance enhancing effects of hordenine in conjunction with other performance enhancing substances, several of which are included in Time 4 Pre-workout Professional.
For example, Hoffman and colleagues (60) examined the effects of a pre-exercise supplement comprising hordenine, caffeine anhydrous, beta-alanine and a form of tyrosine, amongst other ingredients, on reaction time and anaerobic power and subjective feelings of energy, fatigue, alertness, in competitive strength/power athletes. The results showed that the supplement produced a significant improvement in reaction time and feelings of focus and energy in comparison to a placebo.
A study Bloomer et al., (61) found that a combination of hordenine, caffeine anhydrous and other ingredients, increased norepinephrine levels, the breakdown of body fat, and metabolic rate in resistance trained men.
How does Hordenine enhance performance pre workout?
Hordenine produces it stimulant and fat burning effects due to its association with norephinerine and tyramine, a substance that acts as releasing agent for the catacholamines (epinepherine and noreephine) and is essential for normal brain and nervous system function.
Hordenine has been shown to increase levels of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (61), which plays an important role in the sympathetic nervous system by, for example, increasing alertness, arousal and attention, the breakdown of fat and increased heart rate, all of which can contribute to improved performance.
It may also act as an inhibitor of norepinephrine uptake by blocking the action of the norepinephrine transporter, which leads to increased norepinephrine levels and increased activation of the sympathetic nervous system (62).

What is Huperzine A?
Huperzine A is a compound which is extracted from the moss Huperzia serrata. Although it was first identified for medicinal use by scientists in the 1980s, it has been used in Chinese medicine for centuries. It is known as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, which means that it stops an enzyme from breaking down acetylcholine, resulting in an increase in acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine is known as the learning neurotransmitter. Consequently, it has been suggested that Huperzine-A may help treat to conditions that interfere with memory and cognition such as Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
As acetylcholine is also involved in muscle contraction, Huperzine A is used by strength athletes to improve performance.
What does the science say about Huperzine-A and exercise?
Huperzine A has been shown to have both direct and indirect effects on performance. For example, Kaczka and colleagues (64) investigated the effects of pre-workout supplement on the anaerobic performance of resistance-trained men. Twenty-three men underwent three randomised, double-blind testing sessions separated by a seven-day break. The participants performed three tests: isokinetic strength, three repetition maximum and strength and Wingate. They consumed either a placebo or pre-workout supplement comprising Huperzine and a number of other ingredients contained in Time 4 Pre-workout Professional, including L-citrulline, beta-alanine, L-tyrosine, anhydrous caffeine and barley–derived hordenine. The results showed that the supplement significantly improved both upper and lower body strength and power output in resistance-trained men in comparison to a placebo.
Huperzine has been shown to increase levels of the neurotransmitter, dopamine, which plays important roles in executive function, motor control, motivation, arousal, reinforcement, and reward. Executive functions are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behaviour. These include attentional control, working memory, inhibition, and problem-solving. The results of a study by Liang and colleagues (65) showed that Huperzine A not only produced significant increases in acetylcholine levels but also dopamine. The authors noted the increase was similar to that achieved with the cholinesterase inhibitor drugs donepezil and rivastigmine. However, the effects of Huperzine were longer lasting.
How does Huperzine A enhance performance pre workout?
Huperzine A appears to enhance performance through its effect on neurotransmitters. It is a natural version of an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. By blocking acetylcholinesterase, huperzine A is helps to increase acetylcholine levels (65), thereby increasing both physical and cognitive performance. It has also been shown to increase dopamine levels (65).

What is AstraGin®?
AstraGin® is a 100% natural compound made from the plants Panax notoginseng, commonly known as Chinese ginseng, and Astragalus membranaceus, a traditional Chinese medicinal plant. It supports increased absorption of a wide range of nutrients, including amino acids, omega-3 fatty acids and creatine, for which it holds a US patent and multiple international patents.
It is commonly used in products that contain poorly absorbed nutrients, such as turmeric, amino acid-based sports supplements, products promoting gut health, and vitamin and mineral supplements. Due to its quality and efficacy, AstraGin® is used by some of the largest brands in the world in over 200 functional foods, beverages, and supplements.
How does Astragin enhance performance pre workout?
AstraGin® does not directly enhance performance. Rather, it increases the absorption of the performance enhancing nutrients by up-regulating the expression levels of absorption transporters and proteins, which allow greater amounts of nutrients to be absorbed into the body. It also promotes gut health, including reduced inflammation in the intestinal lining. For example, Huang et al., (63) found that supplementation with Astragalus membranaceus and Panax notoginseng resulted in a significant increase in plasma levels of the amino acid L-arginine, which has been shown to promote cell growth and exercise performance, and reduced intestinal inflammation
Synergy: The secret of Time 4 Pre-workout Professional
All of the ingredients in Time 4 Pre-Workout Professional have been carefully selected based on the scientific evidence demonstrating their ability to improve performance. Although a number of these ingredients target different physiological mechanisms, they also work together to produce a synergistic effect; i.e., one which is greater than the sum of their separate effects.
For example, the results of the study by Kaczka and colleagues (64) showed that consuming a pre-workout supplement comprising Huperzine, L-citrulline, Beta-alanine, L-tyrosine, Caffeine Anhydrous and Hordenine, all of which are contained in Time 4 Pre-workout Professional, improved upper and lower body strength and power output significantly in resistance-trained men.
Similarly, Hoffman and colleagues (60) found that a pre-exercise supplement comprising Hordenine, Caffeine Anhydrous, Beta-alanine and Tyrosine, amongst other ingredients, produced a significant improvement in reaction time and feelings of focus and energy.
It is this synergism that makes Time 4 Pre-Workout Professional greater than the sum of its parts.

In conclusion
Whether you are an MMA fighter, powerlifter, bodybuilder endurance athlete or games player, the benefits of your training sessions are dependent upon the quality and volume of the exercise performed; consequently, athletes continually search for methods to enhance their performance in training in a bid to maximise gains. In recent years, the use of pre-workout supplements has increased, as science has demonstrated the value of consuming certain nutrients prior to exercise. While much consideration is given to ensuring sufficient energy is available to perform the planned activity, which is undoubtedly vital, optimal performance is often dependent on a number of other factors, both physiological and cognitive. The precise nature and combination of these will depend on the activity undertaken. Therefore, optimising performance is not just about physical aspects but also how we think and feel. Optimising your energy stores is of little value if you lack the motivation and focus to train at your best. This where Time 4 Pre workout Professional can be a value addition to your nutrition strategy. This specially selected range of natural ingredients provides a multipronged approach to pre-exercise nutrition as it enhances both physical and cognitive aspects of performance, including strength, power, endurance, concentration, motivation, focus, attention, and vigilance. We cannot promise that Time 4 Pre-workout Professional will make you a champion, but it will help you to perform at your very best.

