What Are Essential Amino Acids?
What Are Essential Amino Acids?
Here at Time 4 Nutrition, we take an evidence-based approach to the development of all of our products. We make no outlandish claims, but just state the findings of published studies which have investigated the efficacy of the ingredients we use. Therefore, you can be secure in the knowledge that everything we recommend is supported by evidence. We also understand that science changes. Consequently, we change our formulations and develop new products in accordance with advances in understanding to keep you at the cutting edge. So, we are proud to announce the launch of Time 4 EAA Professional.
Achieving the greatest gains in fitness and muscle muscle size and strength not only requires you to optimise your training, but also your nutrition, which can be more challenging. If you consider that you may train once per day, perhaps 5, or even 6 days per week, but need to consume a range of nutrients at multiple times throughout the day, every day. One of these nutrients is the essential amino acids (EEA). These are the building blocks of the proteins we need for muscle growth, repair, and recovery, which need to be consumed regularly and in very specific amounts.
Many supplements are designed to be consumed before a training session, while others are intended for consumption post-exercise, but to optimise performance, recovery and maximise gains, there are certain key nutrients that we need to consume during a workout. Failure to do so means that we are neglecting a potentially important opportunity.
This is where Time 4 EAA Professional can be a valuable addition to you nutrition strategy. Its unique dual-purpose formula sets the standard for a new era of evidence-based amino acid supplements. Firstly, it provides the full range of essential amino acids at levels and a ratio shown to maximise muscle growth and repair. These are accompanied by a variety of additional ingredients to optimise their absorption and effect.
In addition, Time 4 EEA Professional has also been designed to function as an intra-workout supplement, with the inclusion of a specially formulated combination of ingredients, including a bespoke hydration formula, to be consumed while training. Unlike pre-workout supplements that prepare your body for exercise, intra-workout supplements provide specific nutrients necessary to support your body during exercise.
The ingredients in Time 4 EAA Professional have been shown scientifically to provide a range of benefits for health and performance. These include, but are not limited to:
- Increasing muscle protein synthesis(1, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 16, 17, 20)
- Increasing muscle mass (4, 7, 17, 19 32)
- Reducing exercise induced muscle damage and soreness (3, 15, 20)
- Improving exercise performance (19, 20, 23, 30)
- Enhancing post-exercise recovery (3, 5, 16, 18)
- Reducing exercise induced fatigue (2, 20, 39, 40)
- Increasing endurance (19, 23)
- Enhancing the effect of mTOR (5)
- Inhibiting the muscle limiting protein, myostatin (26, 27, 28)
- Reducing muscle loss (20, 23, 25, 26, 27, 28)
- Increasing amino acid absorption (21)
- Increasing focus, alertness and attention (39, 40)
- Enhancing gut health (22)
- Reducing gastrointestinal distress (21, 22)
- Enhancing energy metabolism (33, 36)
- Enhancing hydration and electrolyte balance (37, 38)
- Enhancing blood flow (34, 35)

What does Time 4 EAA Professional contain?
Time 4 EAA Professional is a specially formulated combination of evidence-based ingredients designed to enhance the body’s essential amino acid content, performance and recovery from exercise while providing a range of health and performance related benefits. These include Time 4 Nutrition’s specially blended formula of all 9 essential amino acids needed by the body to optimise muscle growth, repair and recovery, plus Glycine, Glutamine, Taurine, Green Tea Extract (50% EGCG), Sodium Chloride, AstraGin®, Potassium Chloride, Calcium D-Pantothenate, Tri-Sodium Citrate, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folic Acid, and Vitamin B12.
As we look at each of these ingredients in-depth and a selection of the research that supports their use, you’ll begin to see why Time 4 EAA Professional is such a great product and how it can benefit your health and performance.
What are essential amino acids (EAAs)?
Like constructing a house, building and maintaining a healthy, fit, lean and muscular body requires building blocks. In the human body, these are the amino acids, organic compounds composed of nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, which combine to form the various proteins needed by the body for tissue growth and repair.
There are 20 amino acids that make up the estimated 2 million different types of proteins. Of these 20, 9 are referred to as ‘essential’ because they cannot be produced by the body and so must be obtained from dietary sources, such as meat, eggs, fish, dairy products and plant-based proteins (e.g., soy, buckwheat and quinoa).
What do EAAs do?
In addition to tissue growth and repair, EAAs are involved in numerous important functions within the body, ranging from immune function to energy production.
Although they often work together, each EAA performs specific roles:
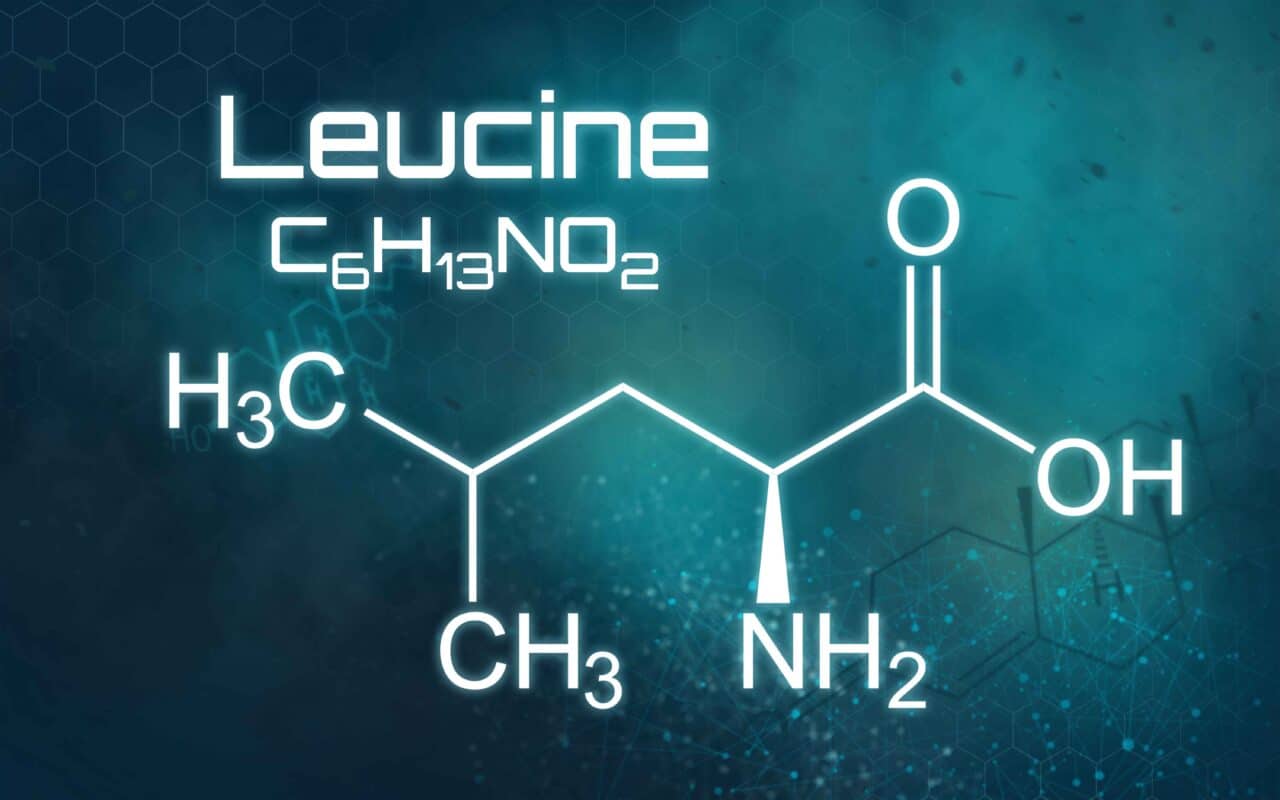
What are the benefits of Leucine?
Leucine is primarily known for its role in muscle protein synthesis and is involved in the mTOR signalling pathway, which regulates cell growth and metabolism. It is leucine which provides the signal to switch from a catabolic state, in which muscle tissue is being broken down, to an anabolic state in which it begins to rebuild. The quicker your body receives this signal after training, the sooner it switches from breaking muscle down to building and repairing it to ensure a full and speedy recovery. Leucine is also involved in many other functions, including the regulation of blood-sugar levels, growth hormone production, and wound healing. It also prevents the breakdown of muscle proteins after trauma or severe stress.
Research shows (13) that to maximise muscle protein synthesis each dose of protein we consume should contain 700-3000 mg of leucine, in addition to a balanced array of the other essential amino acids (EAAs). Just 1 scoop of Time 4 EAA Professional (the intra-workout dose) provides 1500mg of leucine, while 2 scoops (the essential amino acid dose) provide 3000mg. This helps to ensure your leucine requirements are easily satisfied.
Note: Leucine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) along with isoleucine and valine. These amino acids are unique because they have a branch-like molecular structure, which gives them distinct properties and functions.
What are the benefits of Isoleucine?
Isoleucine is concentrated in muscle tissue in humans and has a range of functions. One of its key features is its ability to promote muscle growth and repair, as it is essential for protein synthesis. It helps in the formation of new muscle tissue and facilitates the repair of damaged muscle fibres. Isoleucine also enhances the release of insulin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in muscle growth and recovery. By promoting protein synthesis and insulin secretion, isoleucine contributes to muscle development and maintenance. It may also help to prevent the breakdown of muscle during exercise, and so enhance recovery. In addition, isoleucine also plays a role in regulating blood sugar and energy levels, wound healing, immune function, promoting the secretion of several hormones, and haemoglobin.
What are the benefits of Valine?
Valine plays an essential role in muscle protein synthesis. During intense exercise, it contributes to the supply of extra glucose to the working muscles for energy production, helping to maintain performance and reduce the breakdown of muscle tissue. It also helps to maintain mental vigour, muscle coordination, and emotional calm.
What are the benefits of Phenylalanine?
Phenylalanine plays an important role in muscle protein synthesis and the structure and function of proteins and enzymes. It is also involved in the production of various neurotransmitters such as dopamine, and the catecholamines, epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
What are the benefits of Threonine?
Threonine plays an important role in muscle protein synthesis and the production of collagen and elastin, which support connective tissue. It also aids the synthesis of the amino acids glycine and serine which aid muscle strength and recovery, and plays an important role in fat metabolism and immune function.
What are the benefits of Tryptophan?
Tryptophan is the least plentiful of all 22 amino acids. It plays a role in muscle protein synthesis and is a precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is essential for the regulation of appetite, mood, pain, and the secretion of melatonin, a hormone which regulates sleep and wakefulness. It has also been shown to increase endurance, improve focus, and aid recovery by enhancing sleep.
What are the benefits of Methionine?
Methionine supports muscle repair and growth, contributes to the production of creatine, reduces muscle fatigue during intense workouts and enhances post exercise recovery. It also plays an important role in metabolism and detoxification, reduces cell ageing, prevents the build-up of excess fat in the liver, and is necessary for the absorption of various minerals essential for good health.
What are the benefits of Lysine?
Lysine plays an important role in muscle protein growth and repair, recovery from exercise, energy production, immune function, and hormone, enzyme, collagen and elastin production.
What are the benefits of Histidine?
Histidine is essential for muscle protein synthesis, and plays an important role in immune function and the maintenance of myelin sheaths, a protective barrier that surrounds nerve cells. Histidine is also required for blood cell manufacture. As a precursor to carnosine, histidine benefits muscle function and athletic performance. Carnosine helps to buffer lactate buildup in muscles during intense exercise, helping to delay muscle fatigue and enhancing performance.

The importance of EAAs and muscle protein turnover
The continuous renewal of degraded and damaged muscle protein is important for maintaining muscle mass and function. In the post-absorptive state, or fasting state, (the period when food has been digested, absorbed, and stored) a net breakdown of muscle protein maintains a constant supply of plasma EAAs that provides precursors for protein synthesis in other tissues and organs. In other words, your body breaks muscle down to supply other tissues with EAAs.
The EAAs from dietary intake restore the net loss of muscle protein by stimulating muscle protein synthesis (MPS). In normal conditions, rates of MPS and muscle protein breakdown are equal over the course of the day. If MPS exceeds the rate of muscle protein breakdown, muscle mass will increase over time, with a potential gain in strength.
Accelerated muscle protein turnover (i.e., protein synthesis and breakdown increasing equally) without a gain in net muscle protein mass may also benefit muscle function by replacing older, damaged muscle fibres with new, highly functioning fibres. Therefore, stimulation of MPS/turnover is the principal metabolic basis for increasing strength and physical function. While changes in protein breakdown also play a role in controlling muscle protein metabolism, the stimulation of MPS is the primary basis for the beneficial effects of EAA supplements.
In short, MPS is stimulated by the consumption of EAAs and inhibited by a reduced availability of EAAs in the blood.
Adapted from the International Society of Sports Nutrition (20)
The International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Essential Amino Acid Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle and Performance
While the importance of meeting minimal requirements for each EAA through consumption of high-quality dietary protein intake has been recognised for many decades, the benefits achieved with consumption of free-form EAAs in amounts above and beyond minimal requirements has only become fully appreciated in the past 25 years (20).
In light of the growing body of scientific evidence demonstrating their many benefits, the International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN), an academic society dedicated to promoting the science and application of evidence-based sports nutrition, now provide a position stand dedicated solely to the use of EEA supplementation based on a comprehensive review of the latest research.
Presented here is a selection of some of the key points of the position stand:
- Studies on EAAs’ effects on skeletal muscle highlight their primary role in stimulating muscle protein synthesis (MPS) and turnover. Protein turnover is critical for replacing degraded or damaged muscle proteins, laying the metabolic foundation for enhanced functional performance.
- Supplementation with free-form EAAs leads to a quick rise in peripheral EAA concentrations, which in turn stimulates MPS.
- EAA-based supplements are non-satiating and can be administered alongside food to enhance the anabolic properties of a meal containing a suboptimal dose of protein.
- The safe upper limit of EAA intake (amount), without metabolic disease, can easily accommodate additional supplementation.
- EAAs alone can stimulate MPS and do not require non-essential amino acids.
- Free-form EAA ingestion stimulates MPS more than an equivalent amount of intact protein.
- Repeated EAA-induced MPS stimulation throughout the day does not reduce the anabolic effect of meal intake.
- Even without exercise, EAA supplementation can enhance functional outcomes in anabolic-resistant populations.
- EAA requirements rise when the body is in caloric deficit. During this time, it is essential to meet whole-body EAA requirements to preserve anabolic sensitivity in skeletal muscle.
- EAA stimulation of muscle protein synthesis can occur with multiple dosages and does not interfere with meal effects.
- Individual or groups of EAAs may initiate the stimulatory process; however, significant and sustained stimulation occurs when all EAAs are consumed.
- The effects of EAAs and exercise are interactive, such that the combined effects are magnified. This interaction is due to a greater delivery of EAAs to exercising muscle by increased blood flow and higher blood EAA concentrations.
- Anabolic responses are consistently reported with combinations of EAA ingestion with either resistance or aerobic exercise. This effect is preserved with aging.
- EAA given prior to exercise results in greater anabolism than if consumed after completion of exercise; however, a lesser anabolic effect can be achieved within an hour after exercise cessation.

Do EAAs increase Muscle Mass?
The ISSN (20) state that the most prominent benefit of EAA supplementation is the stimulation of muscle protein synthesis and protein turnover throughout the body, including the synthesis of new muscle protein, which increases muscle mass and quality and, in turn, improvements in physical performance.
Numerous real world studies have demonstrated EAAs ability to increase muscle protein synthesis (1, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 16, 17) and its associated increase in muscle mass (4, 7, 17, 19).
Tipton and colleagues (11) investigated the response of muscle protein synthesis to the ingestion of EAAs after a bout of resistance exercise. The results showed that arterial amino acid concentrations increased approximately 150-640% above baseline during ingestion of EAAs. More specifically, levels of phenylalanine, leucine, and lysine were approximately 160, 640, and 190% greater, respectively, with an EAA supplement in comparison to a placebo. The authors concluded that the ingestion of oral essential amino acids results in a change from net muscle protein degradation to net muscle protein synthesis after heavy resistance exercise similar to that seen when the amino acids were infused.
Vieillevoye et al., (17) evaluated the effects of an EAA supplementation on muscle mass and strength in the early stages of a heavy-load training programme. 29 young males trained for 12 weeks. They were divided into a placebo group and an EAA group. The results of the study showed that EAA supplementation increased both muscle hypertrophy and strength.
These results are not the preserve of the young and fit. As we age, we tend to lose muscle, typically about 3%-5% each decade after age 30. This loss can become more noticeable and start to speed up at around age 60. Over time, this can inhibit an individual’s ability to perform the activities of daily living such as walking, cleaning, shopping, and even dressing, resulting in a loss of independence and an increased risk of falls.
Yoshii and colleagues (7) investigated the relationship between the dietary protein and amino acid intake and resistance training induced muscle hypertrophy among healthy older men. The results showed a significant association between the increase in lean muscle mass and essential amino acid intake. Furthermore, there was also a significant association between the increase in lean muscle and EAA (especially leucine) intake at breakfast among subjects with suboptimal protein intake.
According to the results of a study by Dillon et al., (4), even without resistance training, EAAs can help to increase muscle protein synthesis and lean muscle mass. Using a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled design, considered to be the gold-standard in research, a group of older women received either a placebo or 15g of EAAs per day for 3 months. The results showed that only the women receiving EAA experienced an increase muscle protein synthesis and muscle mass. The anabolic response to EAA supplementation was maintained over time. Interestingly, the EEA group also experienced an increase insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a hormone similar in structure to insulin which plays an important role in muscle growth, metabolism, and protein synthesis.

Do EAAs reduce exercise induced fatigue?
Whether you are a body builder, powerlifter or endurance athlete, fatigue is the enemy of performance. It can be caused by a variety of factors such as an increase in metabolic waste products, a reduction in energy supplies, impaired oxygen supply, dehydration, muscle damage, and central nervous system factors, to name just a few. Consequently, many approaches can be taken to reduce it.
Negro et al., (2) investigated the acute effects of a single oral dose of an EAA enriched mixture on fatigue and maximal force production after resistance exercise that involved training to failure. The results of the study showed that following the resistance exercise there was a significant decrease of strength observed in the placebo group while no statistical differences were found in the EAA group between pre and post test scores. The measure of endurance was also better in the EAA group. Although a significant increase in blood lactate was found in both groups, a higher level was observed in the placebo group compared to the EAA group. The authors suggest acute supplementation with EAA can help to reduce the loss of maximum strength, endurance capacity and the peripheral muscle fatigue resulting from demanding resistance training.
Do EAAs enhance post-exercise recovery?
It is often said that you can only train as hard as you can recover. The more fully and quickly you recover from a training session, the sooner you can train again and more intensely. A number of studies have demonstrated supplemental EAAs ability to enhance recovery beyond stimulating muscle protein synthesis (3, 5, 16, 18).
Matsui and colleagues (3) found the consumption of an EEA supplement suppressed the exercise-induced elevation of muscle damage markers in blood resulting from resistance training. This suggests that EAAs can attenuate muscle damage and therefore aid muscle recovery.
A study by Gee and Denel (18) investigated the effects of supplementation with just 3 of the essential amino acids (leucine, isoleucine and valine) on recovery of power-producing ability following a strength training session. Eleven resistance-trained males, performed baseline measures of a countermovement jump and a seated shot-put throw to assess power. They were then provided with either the amino acid supplement or a placebo to be consumed before and after a strength training session. The counter-movement jump and seated shotput throw were repeated 24 hours after the strength session. The results showed that the amino acid supplementation attenuated the decrease in power that occurred in comparison to a placebo. The authors suggest that use of an amino acid supplement is an effective ergogenic aid for athletes who require improved recovery of power-producing ability following intensive strength training.
EAA supplementation has not only be shown to enhance recovery from strength training, but also endurance. The increased protein requirement of endurance athletes may be related to the need to replace exercise-induced oxidative losses of certain essential amino acids (16). The results of a study by Kato et al., (16) suggest that sufficient levels of EAAs must be consumed to meet the demands of whole-body protein synthesis during recovery from endurance exercise. Failure to do so, will inhibit the recovery process.

Can EAAs reduce muscle damage and soreness?
A little muscle soreness can be a good thing, as a certain amount of muscle tissue damage is required to stimulate growth. However, if the soreness is excessive or prolonged, it can delay recovery and inhibit our ability to train.
A study by Nosaka et al., (15) investigated the effect of supplemental EAAs on muscle soreness and damage. Participants were given an EAA containing supplement before and after exercise and 8 more occasions over a 4-day post-exercise period. Changes in muscle soreness and indicators of muscle damage were assessed for 4 days following exercise. The results showed that indicators of muscle damage, such as myoglobin and plasma creatine kinase, and muscle soreness were significantly lower for the EEA group compared to the placebo.
Can EAAs increase endurance?
While the benefits of EAA supplementation for muscle growth and accompanying increases in strength are well documented, less well known are the beneficial effects of EEAs on endurance. Although resistance training is the most powerful means to improve muscle mass and strength, it does not generally lead to improvements in endurance. However, free essential amino acids (EAAs) act as precursors to a number of the proteins that could potentially produce gains not only in strength but also endurance.
Jang and colleagues (19) investigated the effects of daily consumption of a dietary supplement of EAAs with resistance training on endurance and strength. The subjects in the study were mice. Using animals subjects helps to eliminate the placebo effect, i.e., experiencing changes due to the belief that an intervention is having a beneficial effect even if the intervention is inactive or a ‘dummy.’
The results showed that EAAs plus resistance training produced a 26% greater increase in endurance compared to resistance training alone. Mice consuming EAAs with resistance training also achieved 10% greater gains in muscle and 6% greater gains in strength compared to resistance training alone, which was due to an increased rate of muscle protein synthesis. Resting glucose metabolism also improved.
Getting the most bang for your buck: Optimising the benefits of EAAs
It is easy to assume that if we eat the recommended amount of key nutrients, such as protein, we are bound to gain their full benefits. However, two people may consume an identical diet but the benefits they receive may differ depending on the health and effectiveness of their digestive system. Although free amino acids do not need to be digested in the same way as a high protein food such as steak, which first needs to be broken down into its individual constituent amino acids, they still need to be absorbed through the walls of the small intestine into the bloodstream for use throughout the body.
How fully EAAs are absorbed will determine how many become available in the blood stream to be up-taken by the muscles. Our ability to do this, can be impaired due to a number of factors such as aging, poor diet, stress, lifestyle, certain medications and digestive disorders.
To ensure you get the maximum benefit from Time 4 EEA Professional we have added a number of substances which aid the process of digestion and absorption. Principally, these are glycine, glutamine, Astragin®, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12. Others also contribute to enhanced digestion and absorption in a variety of ways.
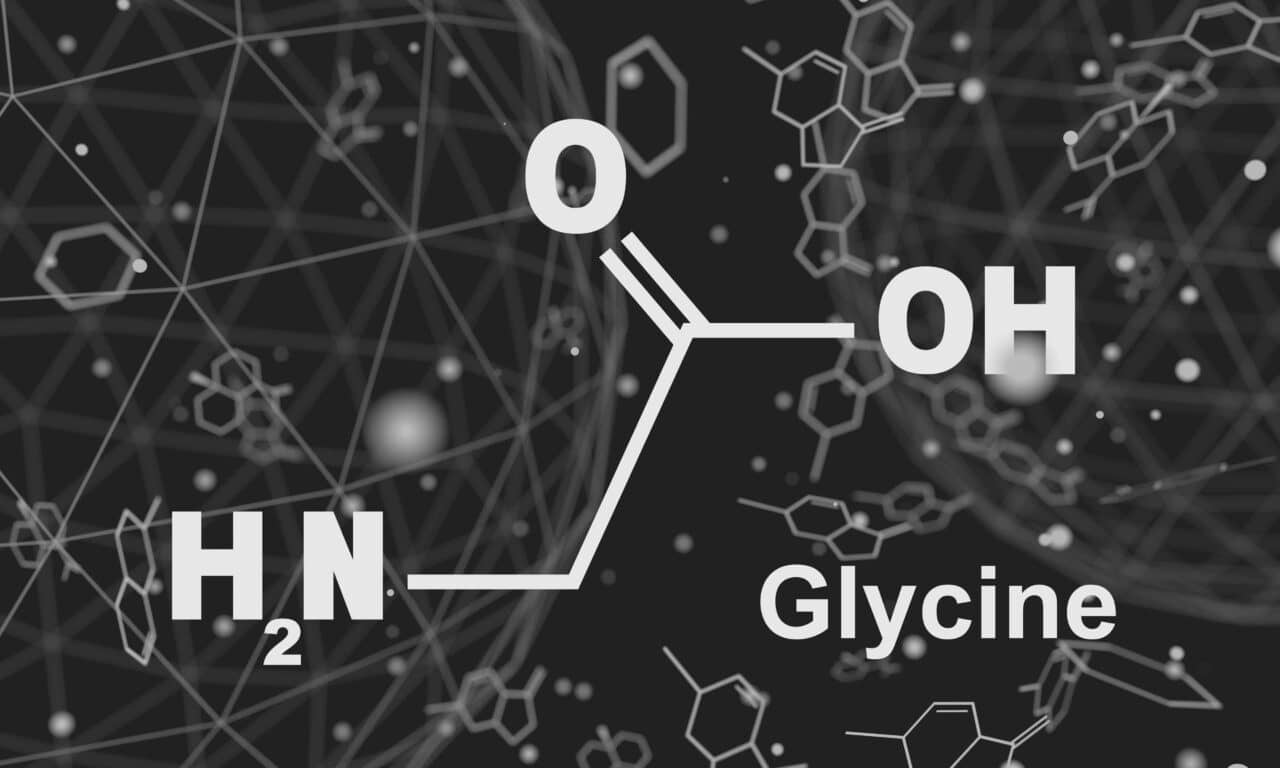
What is Glycine?
Glycine is an amino which plays an important role in many processes essential for good health and optimal performance. These include protein synthesis (constitutes 1/3 of amino acids in collagen and elastin), reducing muscle wasting, the formation of creatine, production of the master oxidant glutathione, improving heart health and enhancing sleep. It has been shown to enhance the absorption of the EEA, leucine, which, as we saw earlier, provides the signal to switch from a catabolic state, in which muscle tissue is being broken down, to an anabolic state in which it begins to rebuild. A study by Ham and colleagues (21) found that leucine failed to stimulate muscle protein synthesis in mice suffering with muscle wasting when pre-treated with the amino acid alanine. However, when mice were pre-treated with glycine, protein synthesis was stimulated significantly by leucine (+51%). Glycine also helps to protect against gastrointestinal distress and assist nutrient uptake during intense exercise, both of which enhance the benefits of EEAs.
It is important to note that while Glycine is not an essential amino acid, it is considered to be ‘conditionally essential’. This means that although the body can produce it, under certain circumstances, including rapid growth, severe stress, trauma, or illness and even during periods of demanding training, the body’s demand for glycine exceeds its ability to produce it. In fact, there is evidence that it is almost impossible to satisfy our daily requirements for glycine even from food when engaged in high intensity exercise. Hence the need for supplementation.
What is Glutamine?
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the human body, accounting for approximately 60 percent of our skeletal muscle. It supports the gastrointestinal tract during exercise by maintaining gut barrier integrity, reducing inflammation, and aiding nutrient absorption. It helps replenish glutamine levels depleted during intense activity, preventing gut permeability, protecting against exercise-induced digestive issues, and supporting immune function in the vulnerable post-workout period.
A review by Achamrah et al., (22) highlighted the key role glutamine plays in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier. The results showed that it is able to modulate intestinal permeability in several conditions including irritable bowel syndrome. While depletion of glutamine results in a number of gut related issues, supplementation with it has been shown to improve gut barrier function.
What is Taurine?
Taurine is an amino acid which is highly expressed in various tissues, including skeletal muscle. It plays an important role in numerous processes essential for health, performance and recovery, including reducing muscle damage and delayed onset muscle soreness, maintaining fluid-electrolyte balance, regulating minerals including calcium within the cells, supporting the general function of the central nervous system, regulating the immune system and enhancing cardiovascular function and dilation of the blood vessels to increase blood supply.
A review by Kurtz et al., (23) investigated the effects of taurine on sports and exercise performance. The results showed improvements in VO2max, time to exhaustion, 3 or 4 km time-trial, anaerobic performance, muscle damage, peak power, and recovery. Taurine also caused a positive change in metabolites. These include a decrease in lactate, creatine kinase, phosphorus, inflammatory markers, and improved glycolytic/fat oxidation markers.
In addition, taurine has been shown to reduce muscle loss. The results of a study by Doss et al., (24) demonstrated taurine’s ability to inhibit the expression of two key molecules involved in the atrophy process, known as atrogin-1 and MuRF-1.
Barbiera and colleagues (25) found that supplementation with taurine had a positive effect on various signalling pathways known to be dysregulated in sarcopenia, i.e., the loss of strength and muscle associated with ageing. In light of these findings, the authors suggest that taurine supplementation may represent a strategy to delay the loss of muscle mass and functionality as we age.

What is Green Tea Extract (Camellia sinensis)?
Green Tea extract is the concentrated form of unfermented tea originating from Asia. It differs from black tea because it retains the original chemical components of the tea plant. Immediately after plucking, heat treatment of the leaves preserves the various pharmacologically active components from biodegradation. After ingestion, these are absorbed by the body and provide a range of health and performance enhancing effects. This has led to Green Tea’s increasing popularity as a healthy beverage and its inclusion in various functional foods.
The green tea extract used in Time 4 EAA Professional has been specially selected due to its high flavonoids content, particularly Epigallocatechin (50% EGCG) and its effect on muscle growth. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is the most abundant catechin component in green tea. Its many benefits include inhibiting the activity of the myokine, myostatin, a type of regulating protein released by muscles, which suppresses muscular growth. Opposing myostatin is a myokine called follistatin. Unlike myostatin, follistatin promotes muscle growth by binding to the myostatin receptor and inhibiting the function of myostatin.
By shifting the balance between myostatin and follistatin in follistatin’s favour, we can stimulate greater muscle growth.
A number of studies have demonstrated epigallocatechin-3-gallate’s ability to achieve this (26, 27). Chang et al., (26) found that supplementation with EGCG reduced muscle loss by inhibiting the activity of myostatin and other mechanisms including the MuRF1 and Atrogin-1 pathway. Similar results were achieved in a study by Meador (27) on rats, which showed that in comparison to younger adult animals (6 months), Murf-1 and myostatin levels were increased between approximately 4- and 12-fold in the older rats who did not receive EGCG controls, but only up to approximately 2-fold in those that received the EGCG.
Epicatechin is another type of flavonoid found in green tea extract. It has also been shown to reduce the activity of myostatin and in addition, increase the activity of follistatin (28).
What is AstraGin®
AstraGin® is a 100% natural compound made from the plants Panax notoginseng, commonly known as Chinese ginseng, and Astragalus membranaceus, a traditional Chinese medicinal plant. It supports increased absorption of a wide range of nutrients, including amino acids, omega-3 fatty acids and creatine, for which it holds a US patent and multiple international patents.
AstraGin® increases nutrient absorption by up-regulating the expression levels of absorption transporters and proteins, which allow greater amounts of nutrients to be absorbed into the body. It also promotes gut health, including reduced inflammation of the intestinal lining.
It is commonly used in products that contain amino acid-based sports supplements, products promoting gut health, and vitamin and mineral supplements. Due to its quality and efficacy, AstraGin® is used by some of the largest brands in the world in over 200 functional foods, beverages, and supplements.

What is Vitamin B6?
Vitamin B6, also known as Pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in over 150 biochemical reactions. A review by Stach and colleagues (29) highlighted the role B6 plays in many functions important for both good health and optimal performance and recovery. These include the metabolism of protein, fats and carbohydrates, including the breakdown and formation of amino acids, energy production, reduction of tiredness and fatigue, immunity, cellular signalling, the regulation of hormonal activity, function of the nervous system, formation of red blood cells and the metabolism and transport of iron. It also plays a role in the absorption of amino acids in the small intestine, and contributes to normal psychological function.
Although vitamin B6 occurs naturally in foods such as milk, salmon, eggs, bananas, chickpeas, and avocado, it is often lacking in the average western diet. This not only has implications for our health but also our ability to exercise. A study by Wolf and Manamore (30) showed that active individuals with poor or marginal nutritional status may have decreased ability to perform high intensity exercise. To further compound the situation, current research suggests that exercise may increase the requirements for vitamin B-6 (30). In light of this, the authors suggest athletes who have poor diets, especially those restricting energy intake or eliminating certain food groups, should consider supplementing.
What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin, which plays an important role in many processes essential for good health and optimal performance and recovery. It has been specially selected for inclusion in Time 4 EAA professional due to its ability to enhance energy production and reduce fatigue, allowing you to maintain performance during demanding high-intensity training sessions. It aids digestive health by helping to maintain the lining of the gut and encourage a healthy balance of bacteria, which aids the absorption of nutrients.
Approximately 6% of people in the UK under 60 years are vitamin B12 deficient with this figure rising to 20% in people aged over 60 years (31). Vitamin B12 deficiency can occur if the body does not absorb a sufficient amount from the gastrointestinal tract or when there is an insufficient dietary intake. This is more common in people who follow vegan diets and to a lesser extent, vegetarian diets.
It may also be due to a range of other issues such having an allergy to vitamin B12 containing foods such as eggs, milk, fish, have a family history of vitamin B12 deficiency or autoimmune disease (31). This not only has implications for your health, such as an increased risk of a variety of problems ranging from impaired red blood cell production and a loss nerve function to psychiatric abnormalities, but can also lead to a reduction in exercise performance due fatigue and weakness.
A recent study by Zhao and colleagues (32) found that those subjects with good vitamin B12 status had greater muscle mass, strength, and function in comparison to those exhibiting lower levels.
What is Niacin?
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3 or Nicotinamide, is a water-soluble vitamin that helps to optimise exercise performance and recovery in a number of ways. These include enhancing the metabolism of protein, fat and carbohydrate for energy production, and increasing the blood supply to the working muscles, which enhances the delivery of oxygen and nutrients. It also aids tissue repair, protects cells from oxidative stress and enhances sleep.
Research shows (33) that nicotinamide performs many of its functions via its role in forming the coenzyme NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). This is crucial for the production of energy and cellular function, as it aids the conversion of the food we consume into fuel for exercise. It also aids muscle protein synthesis and stimulates the production of mitochondria. These tiny organs known as the ‘powerhouses of the cell’, as they provide 90% of the energy needed to sustain life by converting carbohydrate, fats, and proteins we eat, into forms of chemical energy the body can use.

What is Folic Acid?
Folic acid is the synthetic form of folate, a type of vitamin B9. It plays a vital role in many processes in the body essential for optimal performance and recovery. These include amino acid metabolism, muscle growth and repair, energy production and blood flow.
Romero et al., (34) found that the consumption of folic acid increased blood flow to working muscles during resistance exercise by enhancing dilation of the blood vessels.
The results of a study by Stanhewicz and Kenney (35) showed that supplementation with folic acid increases the production and bioavailability of nitric oxide (NO). This is a molecule which causes vasodilation of blood vessels by relaxing the smooth muscle cells within their walls. The results also showed that this may improve the function of the inner lining of the blood vessels, known as the endothelium, which helps to control their contraction and relaxation to regulate blood flow and pressure, and therefore, prevent or reverse the progression of cardiovascular disease.
What is Calcium D-Pantothenate?
Calcium D-Pantothenate is a form of vitamin B5, also known as pantothenic acid. It is an essential nutrient that occurs naturally in some foods, added to others, and available as a dietary supplement. It contributes to exercise performance and recovery in a number of ways. These include metabolising carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to maintain energy levels during intense physical activity, enhancing muscle protein synthesis to aid recovery, and regulating the production of hormones involved in metabolism and energy production. It is often referred to as the ‘anti-stress vitamin’, as it helps to produce stress-related hormones in the adrenal glands, which can be beneficial during strenuous exercise.
Research (36) shows that vitamin B5 performs many of its functions through its role as the precursor of an essential molecule called Coenzyme A (CoA) via the biosynthetic pathway. This means that it is the starting material in the series of steps that eventually lead to the creation of CoA.
CoA is not only essential for energy production, but also for the production of a neurotransmitter needed for muscle contraction and brain function, and is involved in various anabolic processes including muscle protein synthesis. In short, without vitamin B5 there would be no CoA.

Hydration: The often neglected aspect of nutrition
People often pay great attention to their nutrient intake in terms of how much and when to consume protein, fats, and carbohydrate and perhaps certain vitamins and minerals, even supplementing when they feel necessary. Yet when it comes to hydration, they often just rely on their thirst as an indicator of when and how much fluid they should consume. However, this approach can not only hinder their performance in the gym but also their long-term gains. For example, dehydration of just 2% or more of body mass can reduce endurance performance and result in a loss of strength and power, and cause premature fatigue. It can also impair cognitive function, resulting in poorer attention, reaction time and decision-making skills. In addition to increasing the risk of injury and impairing post-exercise recovery. If you are relying on thirst to tell you when to drink, it may already be too late, as it is not typically triggered until we are already dehydrated by approximately 1-2%.
Research shows (37) that when athletes rely on thirst alone, they do not drink sufficient fluid voluntarily to prevent dehydration during exercise. This is exacerbated by the fact that the majority begin training or competition in a somewhat dehydrated state.
A number of studies have demonstrated the profound effect hydration has on performance.
Choi et al., (38) compared the effects of regular water consumption and an electrolyte drink on exercise capacity and recovery after exhaustive exercise. The results showed that consumption of an electrolyte drink increased body capacity to retain water, improved exercise ability, and reduced exercise-related fatigue compared to water alone.
Another study (37) found that maintaining hydration and electrolyte (sodium) levels through consumption of an appropriate beverage improves anaerobic power, attention and awareness, and heart rate recovery time.
To help you stay hydrated during demanding training sessions and maximise performance, we have included a mixture of electrolytes. These are essential minerals which are crucial for a number of functions including maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, muscle contraction, and acid-base balance (pH), which are all important for health and performance:
What is Tri-Sodium Citrate?
Tri-Sodium Citrate is an electrolyte that helps to maintain the balance and absorption of other electrolytes and nutrients,which is crucial for optimal hydration and muscle function during exercise. It also acts as a buffering agent, helping to neutralise lactate produced during intense exercise, which reduces muscle fatigue and improves endurance.
What is Sodium Chloride?
Sodium chloride is a key electrolyte that helps to maintain fluid balance. It enhances the body’s ability to retain water, which is crucial for staying hydrated during and after exercise, and plays a vital role in nerve function and muscle contraction, helping to prevent cramps and maintain performance during prolonged exercise.
What is Potassium Chloride?
Potassium chloride is a crucial electrolyte that helps to maintain fluid balance, nerve and cardiac function, and muscle contraction. It works in conjunction with sodium to regulate the body’s hydration levels. This is vital for overall performance and recovery, and helps to ensure muscle function by preventing muscular fatigue and cramps, which can be common during prolonged and demanding exercise.

Synergy: The secret of Time 4 EAA Professional
All of the ingredients in Time 4 EAA Professional have been carefully selected based on the scientific evidence demonstrating their ability to improve performance. Although a number of these ingredients target different physiological mechanisms, they also work together to produce a synergistic effect; i.e., one which is greater than the sum of their separate effects.
For example, the EAAs are included at a level and at ratios shown to be most effective at stimulating MPS, including a higher leucine content.
The inclusion of glycine, glutamine, Astragin, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 aid the process of digestion and absorption to ensure you get the maximum amount of EAAs into the blood stream.
Epigallocatechin in Green Tea extract helps to inhibit the effects of the muscle limiting protein, myostatin, and along with taurine, helps to reduce the expression of two key molecules involved in the atrophy process to protect against muscle loss.
The B vitamins work together to enhance energy production, with each playing its own unique role in the metabolic pathways that convert food into energy.
Similarly, while sodium and potassium have distinct role in the body, they work together to maintain electrolyte and fluid balance and overall hydration.
It is this synergism that makes Time 4 EAA Professional greater than the sum of its parts.
Do I really need an EAA supplement?
It would be very reasonable to assume that supplementing with EAAs would provide no additional benefit, as they can all be obtained from food. However, there are numerous ways in which an EAAs supplement could make a valuable contribute to your nutrition strategy.
For example, if you consume a plant-based diet, you may find it challenging to obtain all of the EAAs in the requisite amounts from plant sources. In this case, supplements can be consumed alongside food to enhance the anabolic properties of a meal containing a suboptimal dose of protein. Also, as they are non-satiating, they will not make you feel overly full or bloated.
Or perhaps you are intolerant of certain sources of protein, such as dairy. In which case, EEAs can provide you with increased muscle protein synthesis without the gastrointestinal disturbances experienced with food.
If you are trying to reduce your levels of body fat while maintaining muscle mass, you will need to boost the amino acid content of your diet. EAAs will allow you to do this, without a significant increase in energy content. Unlike food, an EAA supplement can be consumed easily during a workout to provide a quick rise in EAAs within muscle tissue and stimulate muscle protein synthesis to greater degree that an equivalent amount of intact protein.
You may choose to consume EAAs in the morning on an empty stomach prior to performing fasted cardio to provide a dose of muscle building amino acids. Or perhaps add a flavoured EAA supplement to water to sip throughout the day to provide a drip feed of amino acids and make plain water more palatable without negatively affecting the anabolic effect of your regular meals. Alternatively, you may choose to use EAAs as a light bedtime drink that will provide your recovering muscles with a supply of amino acids throughout the night when you are fasting. Lastly, EAAs are not just for the young and athletic, as they can enhance the muscle mass, strength and functional ability in anabolic-resistant populations, such as the elderly, even without exercise.
Not all Amino Acids are created equal: The benefits of fermented Amino Acids?
Amino acids can be produced by a variety of different methods. One of the most common is via a harsh acid-based process that extracts them from animal products, such as duck feathers, fur, and even human hair.
The amino acids in Time 4 EAA Professional are produced by fermentation. This is a natural process which involves fermenting plant-based ingredients with microorganisms, like probiotic bacteria. The microorganisms use various carbon sources such as glucose and fructose to produce the amino acids. The process is similar to how other fermented food products are made such as yogurt, beer and vinegar. As no animal products are used, and no harsh chemicals or high temperature processes are involved in production, this results in a more natural, superior quality product that is suitable for vegetarians.

Time 4 EAA Professional: The science of split dosing
There is something of a tendency to think that bigger is better. Although this is true sometimes, for example, if you are competitive bodybuilder an 18inch is likely to be judged more favourably than a 16inch arm, but this is not aways true. Such is the case with Time 4 EAA Professional and its high and low dose recommendations.
This is best understood by thinking of peripheral and central, with the muscles being peripheral and the brain, central. The purpose of the higher, or stand-alone EAA supplement, dose (2 scoops: 14g) is to target adaptations in the muscles. This provides the recommended 3grams of leucine plus the full array of other EAAs needed to optimise growth, and will sustain levels of muscle protein synthesis achieved by a previous meal. In addition, other ingredients also contribute to muscle growth, such as Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) suppressing the negative effects of myostatin.
Performing a physical task such as exercise, is not just about the physical aspects but also the mental aspects. If your head is right your body will follow. So, if you are mentally focused, alert and energized, you are likely to perform better.
The cause of fatigue is complex, influenced by both events occurring in the periphery and the central nervous system (CNS). It has been suggested that exercise induced changes in serotonin and other neurotransmitter levels contribute to the onset of fatigue during prolonged exercise (39)
The primary purpose of the lower, or intra-workout dose (1 scoop: 7 grams) is to maintain neurotransmitter concentrations at the optimum levels to ensure sustained attention, reduced mental fatigue and enhanced focus during your workouts. This is achieved by ensuring the right levels of amino acids and electrolytes.
A reasonable question at this point would be, but why is less better?
In short, this is because various amino acids compete for the same transporters in the brain. The absorption and effects of EAAs such as leucine and tryptophan across the blood-brain barrier are highly competitive and can have differing effects on focus and fatigue.
If leucine predominates, it can lead to enhanced alertness and focus due to increased catecholamines, but potentially also result in energy depletion over time. On the other hand, a high concentration of tryptophan can lead to increased serotonin levels, enhancing relaxation but potentially contributing to feelings of fatigue or decreased focus which can negatively impact physical performance and concentration. Serotonin, in particular, has been linked to fatigue because of its documented role in sleep, feelings of lethargy and drowsiness, and loss of motivation (39). That said, increased levels of tryptophan and the resulting increase in serotonin in the recovery phase can you help to relax and sleep, and so aid growth, repair and recovery.
Support for serotonin’s involvement in fatigue can be found in studies where the brain concentration of serotonin has been altered by means of pharmacological agents. When serotonin was elevated in this way, performance was impaired in both rats and human subjects, and in accordance with this, a decrease in the serotonin level produced an improvement in running performance (39).
A review by Bloomstrand (40) highlighted a number of studies that showed that the ratio of free tryptophan to BCAAs (leucine, isoleucine and valine) in the blood increases during and, particularly, after sustained exercise. This favours the transport of tryptophan into the brain and increase in serotonin, which can lead to central fatigue.
Studies also show that the ingestion of BCAAs reduces the perceived exertion and mental fatigue during exercise and improves cognitive performance after exercise. In addition, the ingestion of BCAAs can improve physical performance during exercise in the heat or in a competitive race when the central component of fatigue is assumed to be more pronounced than in a laboratory experiment (40).
Understanding this interaction between various amino acids and neurotransmitters has allowed us to optimise the supplemental intake in Time 4 EAA Professional to support mental performance and minimise fatigue during training. In addition, at the lower dosage, glutamine and glycine will help to mitigate any potential gastrointestinal distress experienced by some people when trying to rehydrate during high intensity exercise.

What Are Essential Amino Acids? – Summary
Time 4 EAA Professional provides the full range of essential amino acids at levels and a ratio shown scientifically to provide numerous benefits for health and performance including maximising muscle growth and repair, reducing muscle soreness and damage, increasing endurance, and reducing fatigue. While amino acids can be produced by a variety of methods, you can rest assured that those used in Time 4 EAA Professional are derived from the natural process of fermentation. To optimise the absorption and effectiveness of the amino acids, we have added a range of supplementary evidence-based ingredients. These include Glycine, Glutamine, Taurine, AstraGin®, Calcium D-Pantothenate, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folic Acid, and Vitamin B12. We have also added Green Tea extract due to its high Epigallocatechin-3-gallate content (EGCG), which helps to inhibit the activity of the muscle growth limiting protein, myostatin.
The benefits of Time 4 EEA Professional do not end there, as it has been designed to function as an intra-workout supplement with the inclusion of a specially formulated combination of nutrients to be consumed during training sessions to help optimise performance and recovery via a range of mechanisms, including increased muscle protein synthesis and nutrient absorption, enhanced energy production and muscle function, and increased blood flow. An often-overlooked aspect of nutrition is hydration. Suboptimal levels are not only associated with a decline in all aspects of performance, such as strength, power, endurance, and cognitive function, but also poor absorption of nutrients including amino acids. To address this, we have included a bespoke hydration formula including a range of electrolytes. This dual-approach not only provides great results in one convenient product, but also saves you the expense of buying two supplements, giving you more ‘bang for your buck’. Whether you are a carnivore or vegan, trying to maximise muscle growth or maintain your muscle mass while getting lean, want to consume it in the morning, sip it throughout the day or use it as bedtime drink to provide a drip feed of amino acids as you sleep, a young athlete aiming to optimise performance or an older person trying to maintain function, you will not have to look too hard to find a place in your nutrition strategy for Time 4 EAA Professional.
Time 4 EAA Professional is suitable for vegetarians and is gluten & soy free.

